Intermittent claudication, defined
as a symptomatic deficiency in blood supply to exercising muscle which
is relieved with rest, is generally a reliable indicator of occlusive
arterial disease. In its severe form, the decrease in local perfusion
can lead to ischemic rest pain or gangrene. The symptoms vary with the
vessels that are involved. For example, cramping in the upper two-thirds
of the calf is usually due to superficial femoral artery stenosis, cramping
in the lower third of the calf to popliteal disease, buttock and hip claudication
to bilateral aortoiliac disease, thigh claudication to common femoral
artery involvement, and foot claudication to occlusion of the tibial or
peroneal vessels. Percutaneous peripheral vascular angioplasty and/or
stenting is an alternative to bypass surgery in many selected cases and
is offered at BIDMC. In addition, the same techniques can be used for
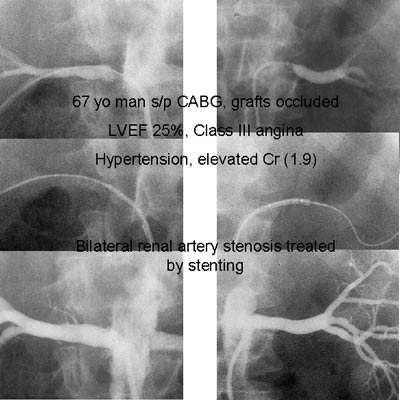
carotid disease, renal
artery disease, Aortic Aneurysms, AV Fistula and malformation, and venous disease, occlusive and thromboembolic.