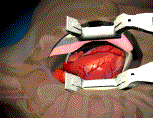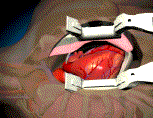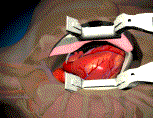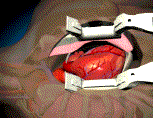
When patients have severe
coronary artery disease not amenable to percutaenous coronary revascularization,
Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery (CABG) is considered, particularely if
left ventricular dysfunction is present. CABG involves a mid-line strenotomy
followed by cardiopulmonary bypass using a heart lung machine. Then, the
left internal mammary artery is taken down and attached to the left anterior
descending artery and saphenous vein graft are taken from the legs and
used to bypass the other arteries. Occasionally, other arterial conduits
are used including the right internal mammary artery and the radial arteries.
CABG results usually in complete revascularization, however, it is a major
procedure. In addition, saphenous vein grafts are prone to atherosclerosis
in 5-10 years (sometimes sooner). This implies that CABG should be avoided
in young patients if possible. Newer techniques include MidCAB and OpCAB
with minimally invasive procedures. Robotic surgery is emerging as
an experimental technique to perform CABG